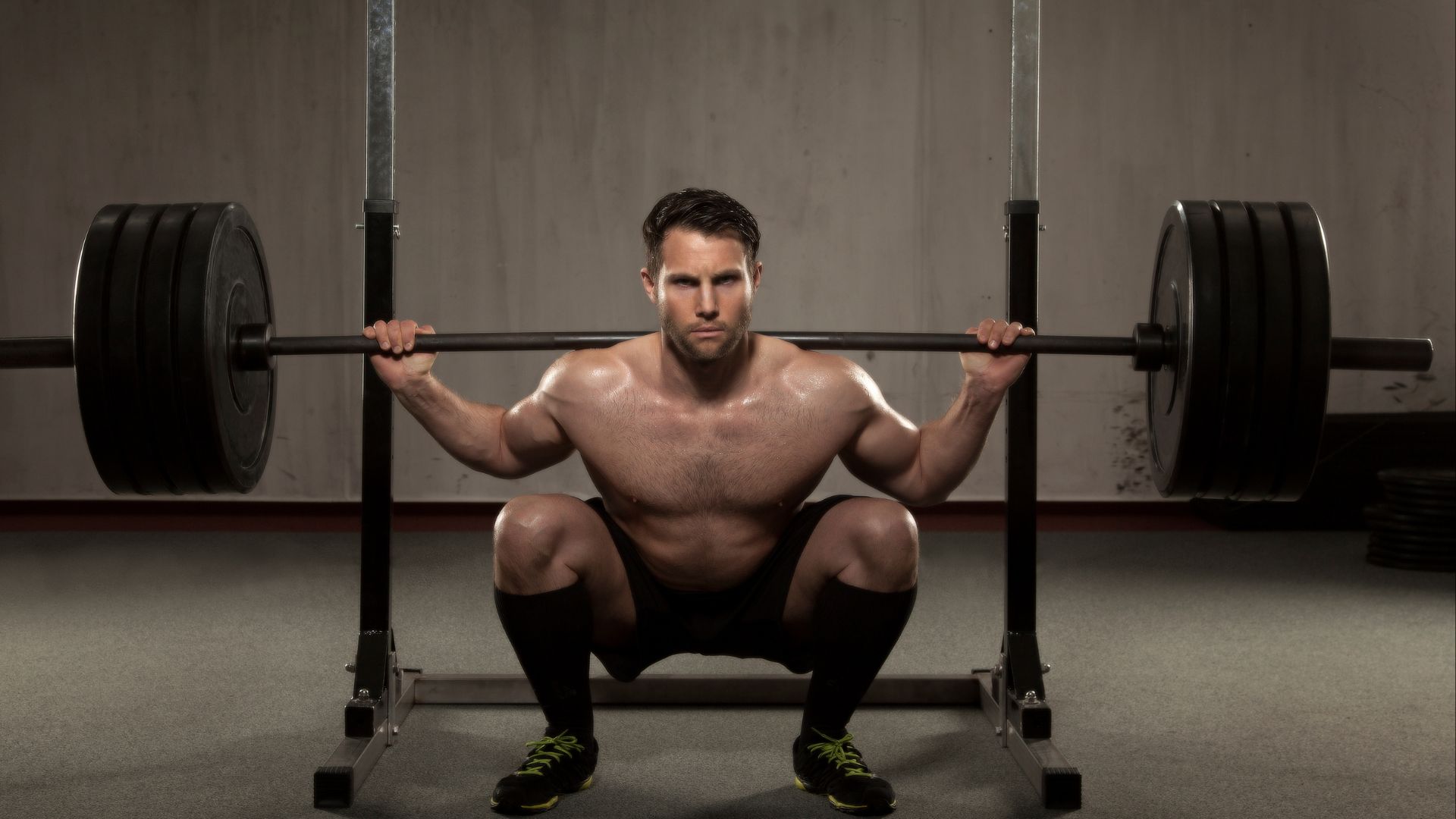
Ever wondered if you should take a deep breath and hold it when you’re about to tackle a low squat? It’s a question that often comes up in the world of fitness.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the pros and cons of holding your breath during this challenging exercise.
So, grab a comfortable seat, and let’s dive into the world of breath control and squats – a topic that can make a significant difference in your workout routine.
Understanding whether or not to hold breath when going down and squat.
Holding your breath while bending down low or squatting is a common practice in weightlifting and some other physical activities.
This technique is often referred to as the Valsalva maneuver. It involves taking a deep breath and holding it to create intra-abdominal pressure, which can provide several benefits including:
Stability: Holding your breath can help stabilize your core and spine during heavy lifts or strenuous activities, reducing the risk of injury.
Increased Strength: The increased intra-abdominal pressure can enhance your lifting performance by providing a stable platform for muscles to work against.
Protection for Your Back: When lifting heavy weights or squatting, holding your breath can protect your lower back by providing additional support.
However, there are some important considerations:
Duration: It’s essential to release your breath after completing the lift or squat.
Prolonged breath-holding can lead to a drop in oxygen levels and increased blood pressure, which may not be safe.
Technique: Proper form is crucial when lifting or squatting. Holding your breath should complement good form, not compensate for poor technique.
Consultation: If you have underlying health conditions or concerns about breath-holding during physical activities, it’s advisable to consult with a fitness professional or healthcare provider.
In other words, holding your breath during low squats or heavy lifts can be beneficial for stability and strength, but it should be done in a controlled and safe manner, with a focus on proper technique and not prolonged breath-holding.
If you have specific fitness goals or health concerns, it’s best to seek guidance from a qualified expert who can tailor advice to your individual needs.

Further explanations.
Let’s dive deeper and elaborate further on all the points mentioned.
First Let’s delve into more detail about how holding your breath can provide stability, increase strength, and protect your lower back during heavy lifts or strenuous activities:
Stability.
Core Activation:
When you take a deep breath and hold it, your diaphragm and the muscles of your abdominal wall contract and tighten.
This action increases intra-abdominal pressure, creating a stable and rigid core.
This stability is essential for maintaining proper spinal alignment and preventing excessive movement of the spine during heavy lifting or squatting.
Spinal Support:
The increased pressure within the abdomen acts like a natural weightlifting belt. It provides additional support to the spine, reducing the risk of injury.
This stability is particularly crucial when lifting heavy loads, as it helps distribute the force evenly and prevents the spine from flexing or twisting excessively.
Increased Strength.
Enhanced Muscle Recruitment:
The higher intra-abdominal pressure created by holding your breath provides a solid foundation for your muscles to contract against.
This stable platform allows for greater recruitment of muscle fibers, leading to increased strength and power output.
Improved Leverage:
The stability generated by holding your breath can improve your leverage during lifts.
For example, during a squat, the stable core and increased intra-abdominal pressure enable you to transfer force more efficiently from your legs to the barbell, resulting in better lifting performance.
Protection for Your Back.
Reduced Stress on the Lower Back:
The added support and stability from breath-holding reduce the load on your lower back.
This is particularly important during exercises like squats, where the lower back is vulnerable to strain due to the heavy load and the bending motion.
With proper breath control, you can minimize the risk of lower back injuries.
Maintained Spinal Alignment:
Holding your breath helps maintain a neutral spine position, which is crucial for spinal health. It prevents excessive arching or rounding of the lower back, which can lead to injuries.
It’s important to note that while holding your breath can offer these benefits, it should be done with proper technique and for brief durations.
Excessive breath-holding or improper form can lead to negative consequences, such as increased blood pressure and potential fainting.
Therefore, it’s essential to learn and practice breath control under the guidance of a qualified trainer to maximize the advantages while minimizing risks.
Additionally, not all exercises require breath-holding, so it’s crucial to understand when and how to apply this technique appropriately in your training routine.
Some important considerations here:
First let’s delve deeper into the importance of releasing your breath, maintaining proper technique, and seeking professional advice when considering breath-holding during physical activities:
Duration.
Release Your Breath:
While holding your breath can provide short-term benefits in terms of stability and strength during heavy lifts or squats, it’s crucial to release your breath immediately after completing the lift or movement.
Continuing to hold your breath for an extended period can have negative consequences:
Oxygen Levels:
Prolonged breath-holding reduces the amount of oxygen available to your body, which can lead to oxygen deprivation (hypoxia).
This can cause dizziness, fatigue, and even loss of consciousness in extreme cases.
Blood Pressure:
Holding your breath increases intra-abdominal pressure, which, when prolonged, can raise blood pressure to unhealthy levels.
Elevated blood pressure can be harmful, especially for individuals with cardiovascular issues.
Technique.
Complementing Good Form:
Holding your breath should never be a substitute for proper technique. Instead, it should complement good form and provide additional support and stability.
Proper technique includes maintaining a neutral spine, engaging the correct muscle groups, and executing the movement with control and precision.
Breath control should not be used as a crutch to compensate for poor form, as this can lead to injuries over time.
Consultation.
Health Conditions:
If you have underlying health conditions, such as cardiovascular issues, respiratory problems, or any medical concerns, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before incorporating breath-holding techniques into your exercise routine.
Some conditions may make breath-holding unsafe or require special precautions.
Professional Guidance:
Seeking guidance from a fitness professional, such as a certified personal trainer or strength and conditioning coach, is highly advisable.
They can assess your individual fitness level, provide instruction on proper technique, and guide you on when and how to use breath-holding effectively in your workouts.
They can also tailor your training plan to ensure it aligns with your specific goals and needs.
In all this, releasing your breath promptly after completing a lift, maintaining proper technique, and consulting with professionals when necessary are critical aspects of safely incorporating breath control into your physical activities.
While breath-holding can offer advantages in terms of stability and strength, it should always be done with awareness of its limitations and potential risks, especially if you have specific health concerns or if you’re new to weightlifting or strenuous exercises.
A concise tabular on this topic here.
Here’s a concise tabular summary of whether you should or shouldn’t try to hold your breath when bending down low during squatting:
| Aspect | Holding Breath during Squats |
|---|---|
| Stability and Core Support | ✔️ Can provide stability and support to the core and spine during heavy squats. |
| Increased Strength | ✔️ Can enhance lifting performance by creating a stable platform for muscles. |
| Protection for Your Back | ✔️ Can protect the lower back by providing additional support. |
| Duration | ❌ Should release your breath immediately after completing the squat to avoid oxygen deprivation and elevated blood pressure. |
| Technique | ✔️ Should complement proper squatting form and not compensate for poor technique. |
| Consultation | ✔️ Advisable to consult with a fitness professional or healthcare provider, especially if you have underlying health conditions. |
Remember that while holding your breath can offer benefits in terms of stability and strength during squats, it should be done with proper technique and for short durations.
Always release your breath after completing the squat and seek professional guidance if you have health concerns or are new to weightlifting.
Conclusion on this topic here.
In conclusion, holding your breath during low squats can indeed provide essential benefits such as stability, increased strength, and protection for your lower back.
However, it is crucial to release your breath promptly after completing the squat, as prolonged breath-holding can have adverse effects on oxygen levels and blood pressure.
Furthermore, breath-holding should never be a substitute for proper squatting technique, and seeking guidance from a fitness professional or healthcare provider is advisable, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
By using breath control judiciously and in alignment with proper form, you can safely maximize its advantages during squatting and other strenuous activities.

Hey there, it’s Mike Rrsq, the Editor-in-Chief over at Jsquat.com, and I’m absolutely obsessed with all things squat fitness! I’ve been lucky enough to get some serious recognition for my work in this field. With a solid background in the fitness and wellness industry, I’ve been there right from the get-go, helping shape this website into what it is today.
You see, I’m not just the boss around here; I’m also a passionate contributor. I love sharing my insights through my articles, and trust me, they’re not your run-of-the-mill stuff. Each piece I write is a labor of love, filled with my expertise and real-world experience in the fitness universe. So, if you’re into fitness and looking for some inspiration, you’re in the right place!