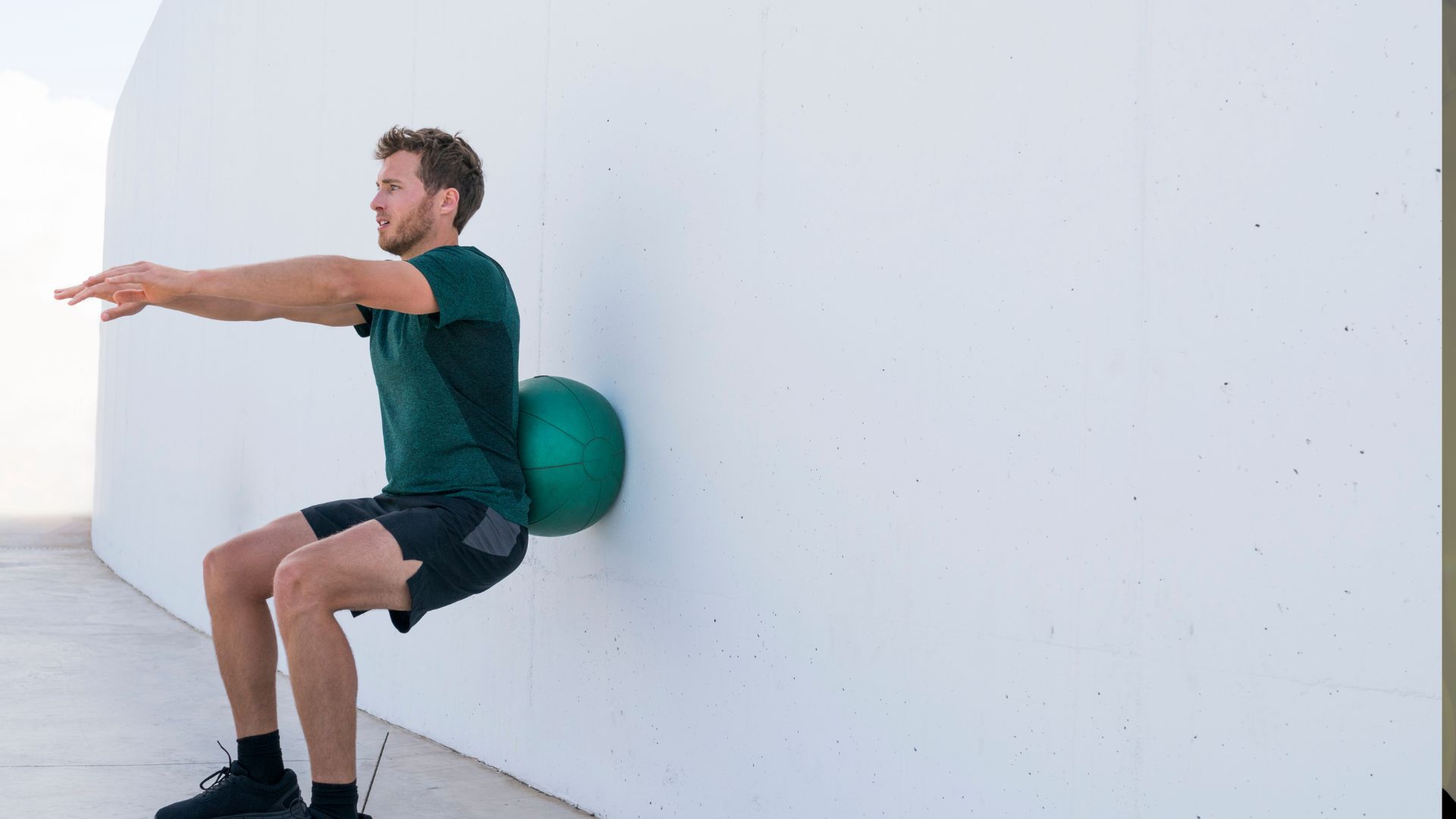
Hey there, posture-conscious readers! Ever wondered how a simple exercise like squatting can have a positive impact beyond just building leg muscles?
You’re in for a treat! In this blog post, we’re diving into the fascinating ways in which squatting can actually help improve your overall posture.
From engaging your core to enhancing hip mobility, there’s more to squats than meets the eye.
So, let’s squat down (figuratively, of course) and explore how this everyday movement can lead to a healthier and more aligned you!
“Squatting can improve overall posture”: Is this true?
Yes, squatting can potentially improve overall posture, but the effects can vary based on several factors such as technique, frequency, and individual differences.
Squatting is a compound movement that engages multiple muscle groups, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, core, and lower back.
When performed with proper form, squatting can contribute to better posture through the following mechanisms.
Here is the thing:
Core Activation: Squats require the engagement of your core muscles to stabilize your spine. This can help strengthen the muscles that support your spine and improve your overall posture.
Hip Mobility: Squatting involves a significant range of motion at the hip joint. Regularly performing squats can help improve hip mobility and flexibility, which can indirectly contribute to better posture.
Spinal Alignment: Proper squatting technique encourages a neutral spinal alignment. This practice can reinforce the habit of maintaining a more upright posture throughout daily activities.

Muscle Balance: Squats target various muscle groups, helping to develop balanced strength in the lower body. This balanced strength can prevent muscle imbalances that might contribute to poor posture.
Note though that squatting can potentially lead to poor posture or even injuries if not done correctly.
Improper technique, excessive weight, or underlying mobility issues can all lead to problems. Additionally, individual biomechanics and pre-existing conditions should be taken into account.
If you’re new to squatting or have any concerns about your posture or technique, it’s advisable to seek guidance from a fitness professional or physical therapist.
Remember that while squats can play a role in improving posture, they are just one component of a holistic approach to posture improvement.
Incorporating a variety of exercises, stretching routines, and mindful awareness of your posture throughout the day can have a more comprehensive impact on your overall posture.
Explanations.
Let’s delve deeper, let me explain these points mentioned further.
Core Activation.
When you perform squats, your body is required to stabilize the spine to maintain proper posture.
This stabilization primarily involves the engagement of your core muscles, which include the muscles of the abdomen, lower back, and pelvis.
As you descend into a squat, your core muscles work to prevent excessive arching or rounding of the spine.
This activation not only helps protect your spine during the movement but also strengthens the muscles responsible for maintaining an upright posture.
As these core muscles become stronger through consistent squatting, they contribute to improved posture by providing better support to your spine and pelvis.
A strong core helps prevent slouching or hunching over, which can lead to poor posture. Additionally, the act of engaging your core during squats reinforces the habit of maintaining proper alignment in your daily activities, further promoting good posture.
Hip Mobility.
Squatting requires a significant range of motion at the hip joint. The movement involves both hip flexion (bending your hips) and hip extension (straightening your hips).
Performing squats with proper form gradually improves the flexibility and mobility of the muscles and connective tissues around the hip joint.
When your hip muscles are more flexible and mobile, you are better able to move through a full range of motion during various activities.
This can include sitting down, standing up, bending over, and walking. Improved hip mobility means you’re less likely to compensate with improper movement patterns that can strain your back or lead to poor posture.

Furthermore,…
Hip mobility can influence the alignment of your pelvis and spine. Tight hip muscles can pull on the pelvis, affecting its positioning.
By working on hip mobility through squats, you can indirectly help maintain a neutral pelvic position, which is crucial for overall posture.
A neutral pelvis aligns…
the spine properly and reduces the risk of postural issues.
In essence, the core activation during squats strengthens the muscles that support your spine and encourage good posture.
The hip mobility gained from squatting helps you move more freely, maintain proper pelvic alignment, and prevent compensatory movements that can lead to poor posture.
It’s important to practice squats with proper form and gradually increase intensity to avoid strain and injuries while reaping these posture-improving benefits.
Spinal Alignment.
Proper squatting technique emphasizes maintaining a neutral spinal alignment throughout the movement.
This means that as you perform a squat, your spine should be in a natural, slightly curved position, with the three natural curves of your spine cervical (neck), thoracic (upper back), and lumbar (lower back)
maintained. This alignment distributes the load evenly across your spinal discs and minimizes stress on the surrounding ligaments and muscles.
By consistently practicing squats with a focus on maintaining this neutral spinal alignment, you reinforce the habit of proper posture.
This habit then extends beyond your squatting sessions and influences how you hold yourself during daily activities.
You become more conscious of your spinal position and are more likely to avoid slouching, rounding your shoulders, or overarching your lower back, all of which can contribute to poor posture.
The awareness you develop during squatting transfers to how you carry yourself while sitting, standing, walking, and lifting objects.
Over time, this heightened awareness and alignment become second nature, leading to improved overall posture.
Muscle Balance.
Squats are a compound movement that engages multiple muscle groups in the lower body, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and even the muscles of the lower back and core.
When performed correctly, squats help promote balanced strength development among these muscle groups.
Muscle imbalances occur when certain muscle groups are significantly stronger or weaker than their opposing counterparts.
These imbalances can pull your body out of alignment, leading to poor posture and potentially causing discomfort or pain.
By incorporating squats into your fitness routine, you are actively working on strengthening both the front (quadriceps) and back (hamstrings and glutes) of your legs.
This balanced development helps stabilize your pelvis and spine, reducing the risk of postural issues that can arise from uneven muscle strength.
Additionally, squats engage your core muscles to stabilize your spine during the movement. This not only contributes to spinal alignment, as mentioned earlier, but also ensures that your core muscles are adequately developed.
A strong core provides a stable foundation for your entire body, which is crucial for maintaining proper posture in various situations.
In other words, proper squatting technique reinforces a neutral spinal alignment that carries over into your daily activities.
Engaging various muscle groups during squats promotes balanced strength development, preventing muscle imbalances that could lead to poor posture.
This comprehensive approach to strength and alignment helps you maintain a healthier and more upright posture overall.
A concise tabular on this topic here.
Here’s a concise tabular comparison of how squatting can improve overall posture, highlighting the key aspects we’ve discussed:
| Aspect | How Squatting Improves Posture |
|---|---|
| Core Activation | Engages core muscles to stabilize spine, strengthening support. |
| Hip Mobility | Increases flexibility, aiding proper movement and pelvic alignment. |
| Spinal Alignment | Promotes neutral spine during squats, reinforcing good posture. |
| Muscle Balance | Targets multiple leg muscles, prevents imbalances and instability. |
Feel free to use this table to quickly reference the ways in which squatting can positively impact overall posture.
Conclusion.
In conclusion, squatting offers a multifaceted approach to improving overall posture.
It engages core muscles for spine stabilization, enhances hip mobility and flexibility, encourages a neutral spinal alignment, and fosters balanced lower body strength.
By incorporating proper squatting technique into your fitness routine, you can develop a stronger, more aligned body that supports better posture in daily activities.
Remember, while squatting is beneficial, it’s essential to prioritize proper form and consider individual factors to maximize its posture-improving effects.

Hey there, it’s Mike Rrsq, the Editor-in-Chief over at Jsquat.com, and I’m absolutely obsessed with all things squat fitness! I’ve been lucky enough to get some serious recognition for my work in this field. With a solid background in the fitness and wellness industry, I’ve been there right from the get-go, helping shape this website into what it is today.
You see, I’m not just the boss around here; I’m also a passionate contributor. I love sharing my insights through my articles, and trust me, they’re not your run-of-the-mill stuff. Each piece I write is a labor of love, filled with my expertise and real-world experience in the fitness universe. So, if you’re into fitness and looking for some inspiration, you’re in the right place!