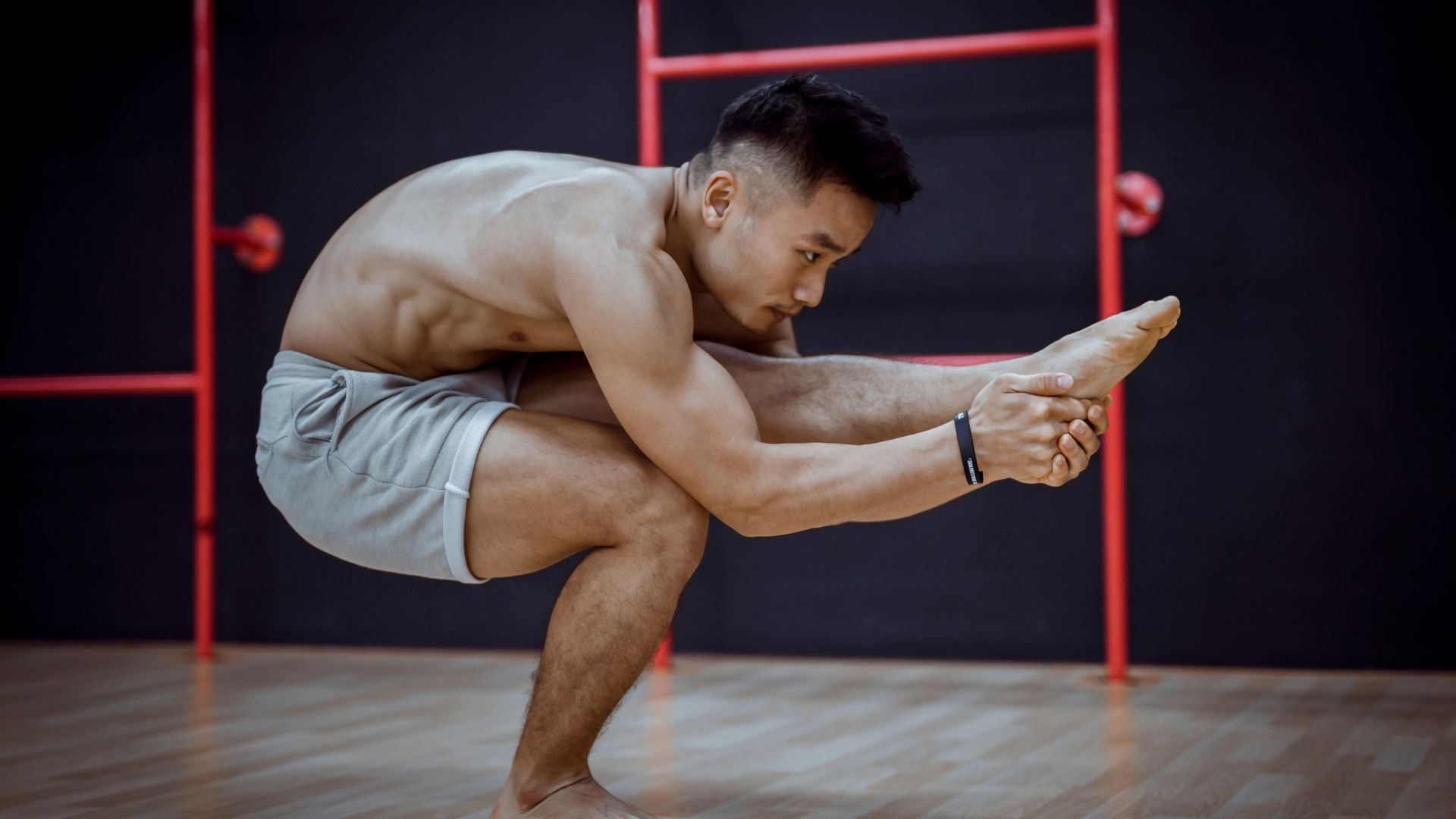
Have you ever noticed how squats can make you feel more flexible? It’s a common phenomenon experienced by many individuals who incorporate squats into their exercise routine.
In this article, we will delve into the reasons behind why squats have such a positive impact on flexibility. From the mechanics of the exercise to the physiological changes that occur in your body, we will explore it all. So, grab a seat (or stand up!) and let’s dive into the fascinating world of squats and flexibility.
Squats make you feel more flexible because they stretch and mobilize your lower body muscles and joints, gradually improving your range of motion. By consistently performing squats, your muscles and connective tissues become more pliable and adaptable. This increased flexibility allows you to move through a wider range of motion, giving you a greater sense of flexibility and ease of movement.
Note that everyone’s body is different, and individual experiences may vary. If you have specific concerns about flexibility or any other aspect of your fitness, it’s always recommended to consult with a qualified fitness professional or healthcare provider.
Increased Range of Motion.
When you perform squats, your body goes through a motion that requires bending your knees and hips.
This bending action helps to stretch and mobilize the muscles and joints in your lower body, including your hips, knees, and ankles.
As you repeatedly perform squats over time, your body adapts to this movement pattern and becomes more accustomed to the range of motion required.
Your muscles, tendons, and ligaments gradually become more flexible and pliable, allowing for greater movement in your joints.
The stretching and mobilization of these muscles and joints during squats help to break up any tightness or stiffness that may be present.
It encourages the muscles and connective tissues to lengthen and elongate, which can lead to an increased range of motion in the hips, knees, and ankles.
By regularly engaging in squats and consistently challenging your body with this movement, you gradually improve your flexibility in these areas.
Your body becomes more comfortable and capable of moving through a wider range of motion, which can contribute to a feeling of increased flexibility.
It’s worth noting that the extent of flexibility improvement can vary from person to person, and it may take time to notice significant changes.
Additionally, incorporating other stretching exercises and mobility work alongside squats can further enhance your overall flexibility.
Stretching the Muscles.
During squats, various muscle groups in your lower body are actively engaged and stretched.
These include the quadriceps (front of the thighs), hamstrings (back of the thighs), glutes (buttocks), and hip flexors (muscles that allow you to lift your legs).
As you descend into a squat, these muscles are lengthened and put under tension. This stretching action helps to increase the flexibility of these muscles over time.
Regular squatting sessions provide a consistent stimulus for these muscles, encouraging them to become more pliable and supple.
When you perform squats, the quadriceps and hip flexors are particularly involved in extending your knees and hips, respectively.
These muscles are actively stretched as you lower your body down into the squat position. The hamstrings, on the other hand, are lengthened as you hinge your hips and lower your torso. The glutes are engaged to provide stability and power during the upward phase of the squat.
By regularly incorporating squats into your fitness routine, these muscle groups are repeatedly stretched and activated. This consistent stretching helps to gradually improve the flexibility of these muscles.
Over time, they become more adaptable to the range of motion required during squats, allowing you to perform the exercise with greater ease and comfort.
The increased flexibility in these muscle groups not only benefits your squat performance but also translates to improved overall flexibility.
Having more flexible quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and hip flexors can enhance your ability to perform other movements and exercises that require similar ranges of motion.
It’s important to note that while squats can contribute to improved muscle flexibility, they should be combined with proper warm-up, cool-down, and stretching routines for optimal results.
Additionally, listening to your body and gradually progressing in the intensity and depth of your squats is essential to prevent injury and promote long-term flexibility gains.
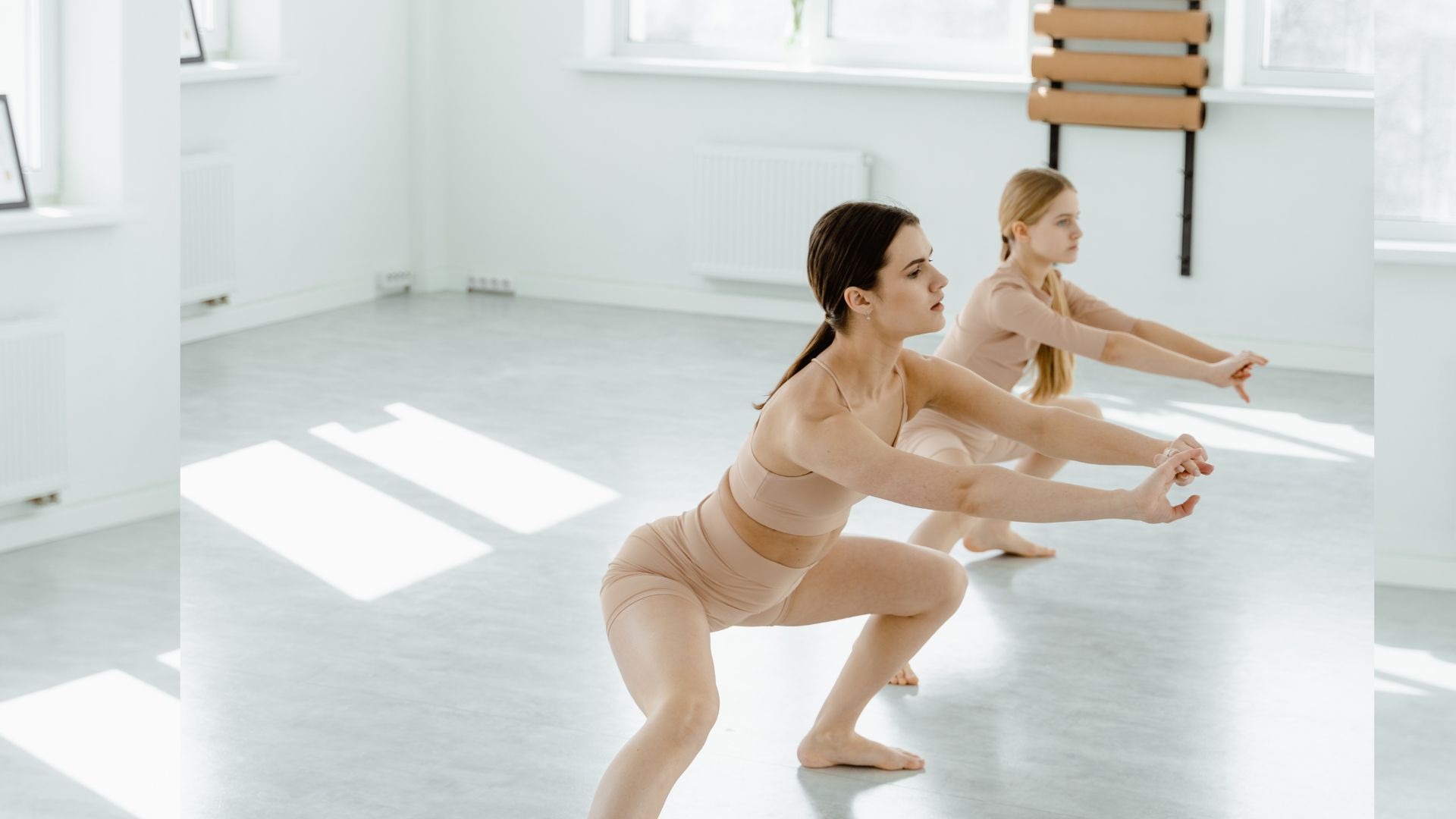

Improved Joint Mobility.
When you perform squats, your joints, including the hips, knees, and ankles, go through a full range of motion. This movement pattern has several benefits for joint mobility and flexibility.
Firstly, squats help to lubricate the joints. The bending and straightening motions involved in squats stimulate the production and distribution of synovial fluid in the joints.
Synovial fluid acts as a lubricant, reducing friction between the joint surfaces. Improved lubrication allows for smoother and more effortless movement, enhancing joint mobility.
Secondly, squats promote increased blood flow to the joints. As you perform squats, the muscles surrounding the joints contract and relax, promoting blood circulation in the area.
The increased blood flow delivers essential nutrients and oxygen to the joint tissues, supporting their health and flexibility.
Furthermore, squats engage the connective tissues, such as ligaments and tendons, surrounding the joints. These tissues play a crucial role in joint stability and flexibility.
The squatting motion helps to stretch and strengthen these connective tissues, making them more adaptable and flexible over time. This can contribute to improved joint mobility and a greater range of motion.
By regularly incorporating squats into your exercise routine, you provide a consistent stimulus for your joints and the surrounding connective tissues.
Over time, this can lead to improved joint mobility, enhanced flexibility, and a greater ability to move comfortably and freely.
It’s important to note that while squats can be beneficial for joint mobility and flexibility, it’s essential to maintain proper form and technique during the exercise to avoid undue stress on the joints.
If you have any underlying joint conditions or concerns, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a qualified fitness instructor for guidance.
Core Engagement.
When you perform squats, your core muscles, which include the abdominals and lower back muscles, play a vital role in stabilizing your body throughout the movement.
This core engagement offers several benefits that indirectly contribute to improved flexibility and range of motion.
During squats, the core muscles are activated to maintain proper posture and spinal alignment. They work to stabilize your trunk and pelvis, preventing excessive movement and maintaining a strong and balanced position.
This stability allows for efficient transfer of forces between the lower body and upper body, enhancing overall movement control.
By regularly engaging and strengthening your core muscles through squats, you can improve your overall posture.
A strong core helps support your spine and maintain proper alignment, which can alleviate any postural imbalances or misalignments that might restrict your flexibility.
Additionally, a stable and well-engaged core during squats helps to distribute the load evenly throughout your body.
This can reduce strain on specific muscles or joints, allowing for smoother and more controlled movements.
With improved stability and load distribution, you may find it easier to perform exercises or activities that require greater flexibility, as your body can move with better control and balance.
Furthermore, a strong core can enhance the coordination and synergy between your upper and lower body movements.
The core acts as a bridge, connecting the power generated from your lower body during squats to the movements of your upper body.
This improved coordination can facilitate better overall movement patterns and contribute to a greater range of motion.
It’s important to note that while squats engage the core muscles, it’s beneficial to incorporate specific core exercises and targeted training for comprehensive core strength development.
This can further enhance the stability, strength, and flexibility of your core muscles.
If you have any concerns about your core strength or how to properly engage your core during squats, consulting with a qualified fitness professional can provide personalized guidance and ensure that you perform exercises correctly and safely.
Improved Muscle Activation.
Squats are a compound exercise that engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously.
By incorporating squats into your fitness routine on a regular basis, you can improve muscle activation and coordination, leading to enhanced body control and increased fluidity and flexibility in your movements.
During squats, various muscles are involved, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, hip flexors, calves, and lower back muscles.
These muscles work together to stabilize your body and execute the squatting motion effectively.
As you perform squats consistently, your muscles adapt and become more efficient at activating and coordinating with each other.
This improved muscle activation allows for better control and synchronization of movement patterns.
By enhancing muscle activation patterns through squats, you develop a greater ability to recruit and engage the relevant muscles during other exercises or activities.
This can positively impact your overall body control, making it easier to move with fluidity and execute movements with precision.
Furthermore, the increased muscle activation and coordination developed through squats can indirectly contribute to improved flexibility.
When muscles are effectively activated and working together, they can generate more power and force, leading to greater joint mobility and range of motion.
Moreover, improved muscle activation patterns can enhance your body’s ability to respond to external stimuli, such as changes in balance or direction.
This increased responsiveness allows for smoother and more coordinated movements, enhancing your overall athletic performance and flexibility.
It’s important to note that while squats are effective in improving muscle activation and coordination, it’s beneficial to incorporate a well-rounded fitness routine that includes a variety of exercises targeting different muscle groups and movement patterns.
This will provide comprehensive development and support for overall flexibility and body control.
If you have specific goals or concerns regarding muscle activation or flexibility, consulting with a qualified fitness professional can provide personalized guidance and help design a training program that suits your needs.
Here’s a tabular breakdown of the information you requested:
| Aspect | Why | How | When | Example | What to Consider |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Squats stretch and mobilize the muscles and joints, improving range of motion. | By repeatedly performing squats, gradually improving flexibility. | Regularly incorporate squats into fitness routine. | Performing deep squats to target hip, knee, and ankle flexibility. | Listen to your body, progress gradually, and maintain proper form to prevent injury. |
| Muscle Stretch | Squats target muscle groups like quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and hip flexors, stretching and improving flexibility in these muscles. | Squats involve bending the knees and hips, activating and lengthening the targeted muscles. | Incorporate squats as part of a well-rounded exercise routine. | Performing squat variations like goblet squats or barbell squats to stretch the muscles. | Ensure proper warm-up and cool-down, and consider incorporating additional stretching exercises. |
| Joint Mobility | Squats require a full range of motion in the hips, knees, and ankles, which enhances joint mobility. | Squatting helps lubricate the joints, improve blood flow, and stretch connective tissues surrounding the joints. | Perform squats regularly, following proper form and technique. | Performing deep squats with controlled movements to improve joint mobility. | Consider any underlying joint conditions and seek professional guidance if needed. |
| Core Engagement | Squats engage the core muscles, leading to improved overall posture and spinal alignment. | Core muscles stabilize the body during squats, maintaining proper posture and alignment. | Engage the core during each squat repetition. | Performing squats with focus on maintaining a strong core and stable posture. | Incorporate targeted core exercises alongside squats for comprehensive core strength development. |
| Muscle Activation | Squats are a compound exercise involving multiple muscle groups, improving muscle activation and coordination. | Regularly performing squats leads to stronger and more coordinated muscle activation patterns. | Include squats as part of a regular fitness routine. | Performing squats with proper form and engaging the targeted muscle groups. | Consider incorporating a variety of exercises targeting different muscle groups and movement patterns. |
Please note that the provided table is for illustrative purposes and the examples mentioned are not exhaustive.
Adjust the exercises and considerations based on your specific needs and consult with a qualified professional for personalized guidance.
Conclusion.
In conclusion, engaging in squats can have several positive effects on your flexibility. By performing squats, you can improve your range of motion in the hips, knees, and ankles, making these joints more flexible over time.
Squats also stretch and activate major muscle groups like the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and hip flexors, leading to increased flexibility in these muscles.
Additionally, squats require a full range of motion in the joints, which helps to improve joint mobility, enhance blood flow, and promote flexibility in the surrounding connective tissues.
Moreover, squats engage the core muscles, contributing to better posture and spinal alignment, indirectly enhancing flexibility and range of motion.
Lastly, regular squatting improves muscle activation and coordination, which enhances overall body control and facilitates fluid and flexible movements.
Remember, individual experiences may vary, and it’s important to listen to your body and progress gradually in your squatting routine.
Incorporating other stretching exercises and maintaining proper form and technique are also essential for maximizing the benefits and preventing injuries. If you have specific concerns or questions about your flexibility or fitness routine, it’s recommended to consult with a qualified fitness professional or healthcare provider.

Hey there, it’s Mike Rrsq, the Editor-in-Chief over at Jsquat.com, and I’m absolutely obsessed with all things squat fitness! I’ve been lucky enough to get some serious recognition for my work in this field. With a solid background in the fitness and wellness industry, I’ve been there right from the get-go, helping shape this website into what it is today.
You see, I’m not just the boss around here; I’m also a passionate contributor. I love sharing my insights through my articles, and trust me, they’re not your run-of-the-mill stuff. Each piece I write is a labor of love, filled with my expertise and real-world experience in the fitness universe. So, if you’re into fitness and looking for some inspiration, you’re in the right place!